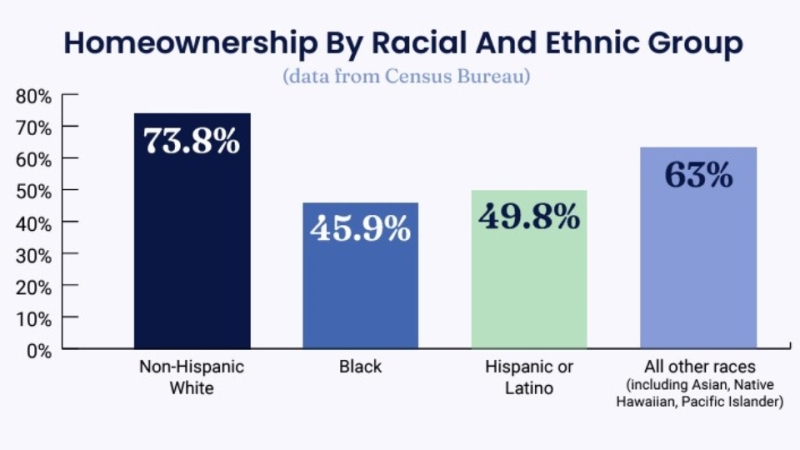
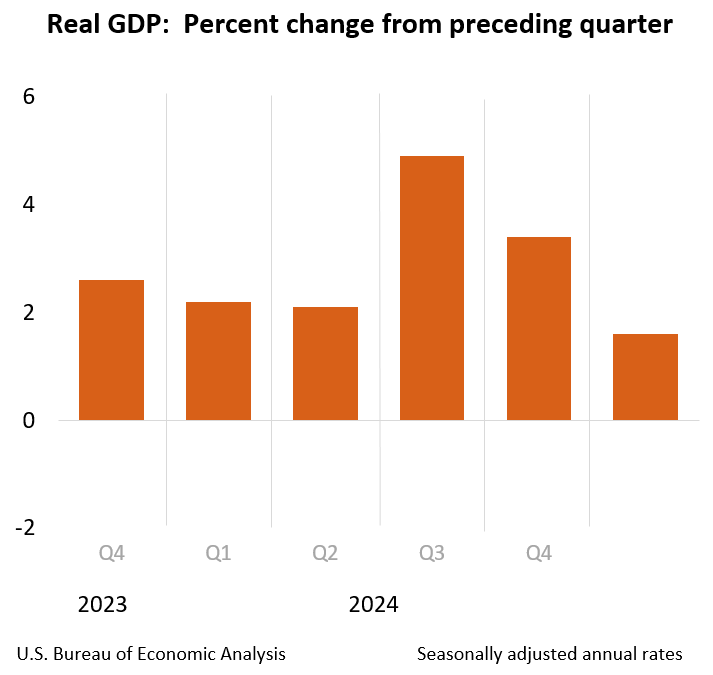
2.38 Million Americans Became First-time Homebuyers In 2020

Genworth Mortgage Insurance released the 15th edition of its First-Time Homebuyer Market Report, for the fourth quarter and full-year of 2020. According to the report, 2.38 million Americans became first-time homebuyers in 2020––up 14% from the same period a year ago.
In Q4 2020, 657,000 single-family homes were purchased––up 26.4% from a year ago. Additionally, Genworth chief economist, Tian Liu revealed that first-time homebuyers reached 2.76 million (seasonally-adjusted annual rate) in Q4, their fastest pace on record. First-time homebuyers represented a bigger share of the housing market. According to the report, for the full year, first-time homebuyers made up (40% vs. 38% in 2019) in the single-family housing market, and a higher percentage of purchase loan borrowers (56% vs. 55% in 2019) in the mortgage market.
"Out of 2020 came a housing boom with rapidly rising home prices and a new construction boom in single-family homes," said Liu. "More recently, despite the COVID-19 pandemic and a deep recession, the U.S. housing market has staged an unexpected and strong rebound in the second half of 2020, resulting in a record number of first-time homebuyers."
Liu also added that first-time homebuyer demographics are maturing. The aging of the Millennial population implies that the increase in first-time homebuyers over the age of 30 may lead to an overall increase in the number of first-time homebuyers in the 25-44 age group, which could be in the order of 580,000 first-time homebuyers over five years, according to the report.
"The pandemic and resulting economic impact increased housing demand in many ways. Working from home, remote learning, and other social distancing measures have forced homes to become the end all be all, ultimately resulting in an increase in a home's value to homebuyers. Large expenditures on travel, leisure, entertainment, and personal services have decreased significantly throughout the pandemic, freeing up disposable income to be used toward housing. While the unemployment rate has increased overall, its impact has been more muted on higher-income earners who are more likely to become potential homebuyers – so the job losses have had less effect on housing," said Liu.
"Potential homebuyers may have benefitted from pandemic-related forbearance programs on student loans, credit cards, and auto loans, temporarily reducing debt repayment for some. The real estate and housing finance industries have successfully maintained the functioning of the housing market by reducing the number of face-to-face interactions in homebuying, selling, and financing. The forbearance program in the mortgage industry prevented foreclosures by borrowers impacted by the pandemic and helped stabilize the housing market. Finally, fiscal stimulus under the CARES Act helped to maintain spending and income levels, which prevented spillover from the public health crisis into a broader economic and housing crisis. Together, all of these factors made 2020 the best year on record for the first-time homebuyer market."
Click here to view the full report.